The Catenary - The Mathematics of a Hanging Chain
Introduction
The catenary is one of the most elegant curves in mathematics and physics. It describes the shape that a uniform chain or cable naturally assumes when suspended between two points under the influence of gravity. While it might seem like a simple problem, the catenary connects deep mathematical concepts and provides a nice example of using physics intution to solve problems.
The Physical Problem
The set-up of this problem is very simple: simply take a chain of length $L$ with some uniform mass density $\rho$ and suspend this between two points that are (at least for now) at an equal height. See the diagram drawn below:
Mathematical Derivation
There are two ways to derive the catenary equation. The first and most simple approach uses a balance of forces on a segment of the chain. This is a classic high school physics problem… lets quickly sketch out the solution:
Setting Up the Problem: Balance of Forces
The first way of solving this problem is with a balance of forces on the chain. Consider a segment of the chain from the bottom (where the chain is horizontal) to some point along the curve. The unknown quantities of our problem are then simply:
- $T_0$: The horizontal tension at the bottom of the chain
- $T_1$: The tension at the upper end of the segment, acting along the tangent to the chain
- $W$: The weight of the segment, acting downward
- $\theta$: The angle that $T_1$ makes with the horizontal
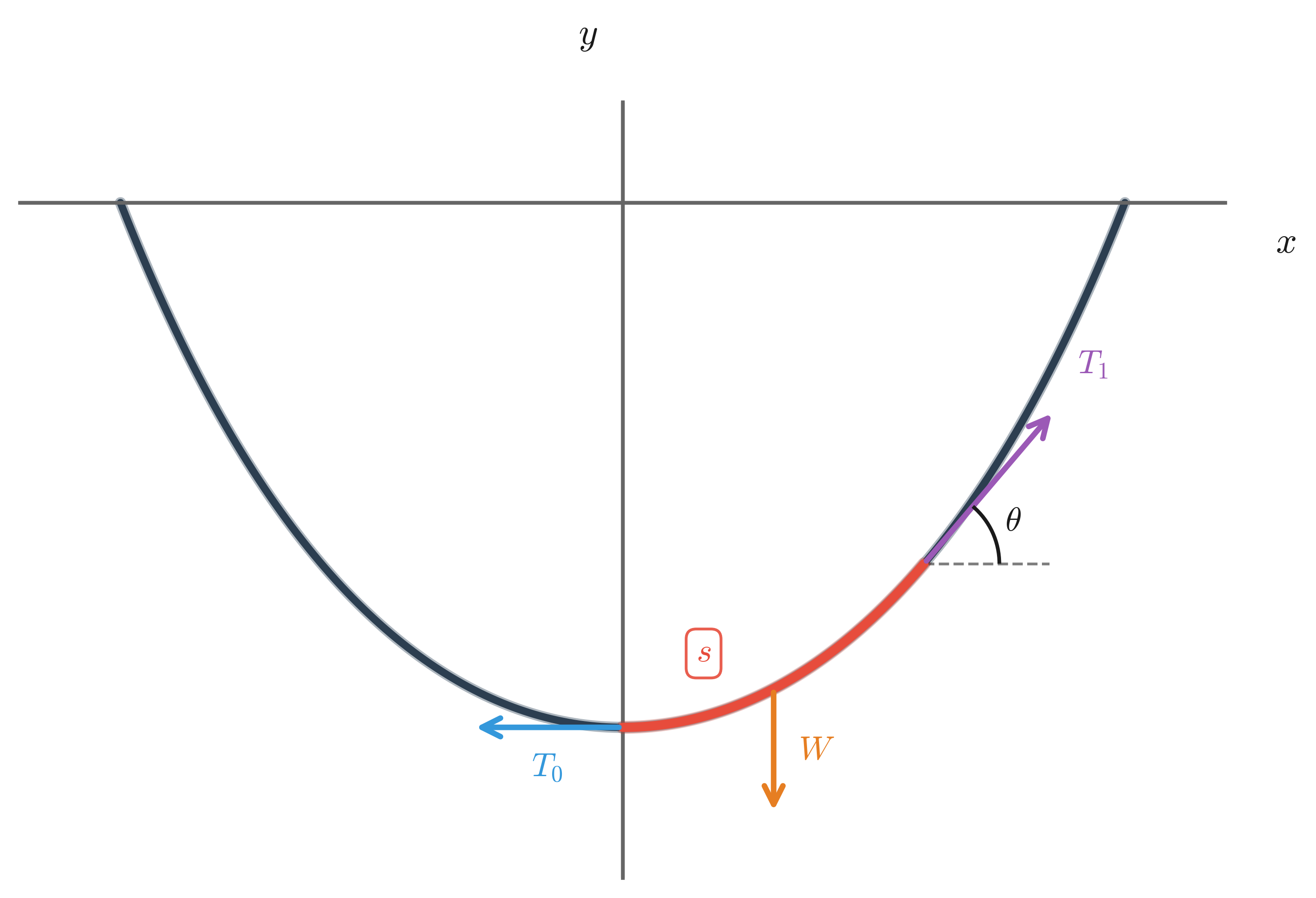
[To be filled: Derivation using force balance equations]
The Variational Approach
[To be filled:
- Minimizing potential energy
- Euler-Lagrange equation
- Derivation of the differential equation]
Solving the Differential Equation
[To be filled:
- The catenary equation: y = a cosh(x/a)
- Physical meaning of the parameter ‘a’
- Boundary conditions]
Physical Intuition
[To be filled:
- Why the catenary shape minimizes potential energy
- The role of tension
- Comparison with other curves (parabola, circular arc)]
Key Properties
[To be filled:
- The catenary is self-similar
- Relationship between sag and span
- Tension distribution along the curve]
Applications
[To be filled:
- Suspension bridges
- Power lines - Other engineering applications]
Visualizations
[To be filled: Link to Jupyter notebook with animations showing:
- How the catenary shape changes with different parameters
- Comparison with parabola
- Dynamic visualization of the hanging chain
- Interactive exploration of boundary conditions]
Interactive Notebook: View the catenary animations and explore the mathematics interactively
Beyond the Simple Case
[To be filled:
- Catenary with different endpoint heights
- Catenary with non-uniform density
- Catenary under additional loads (e.g., suspension bridges)]
Conclusion
[To be filled: Summary of key insights and the beauty of the mathematical solution]
Further Reading
[To be filled: References and resources for deeper exploration]